Wavefront modulation based on photorefractive effect and machine learning
This project was done during my junior and senior years at the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), co-advised by Professor Xiaoye Xu of the CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information and Professor Zhiwei Xiong of the Department of Electronic Engineering and Information Science. Base on this project, my B.Sc. thesis was recognized as an outstanding thesis of USTC for the year of 2022.
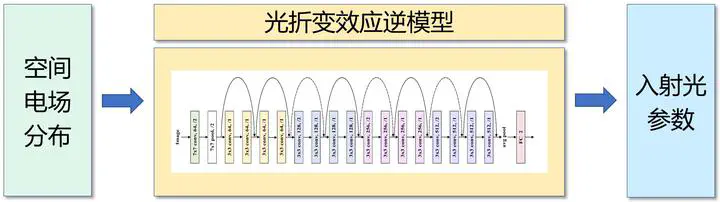
Abstract: With the development of adaptive optics, the wavefront modulation technology has been widely applied in many fields. At present, there are two mature optical wavefront modulation methods: phase plate and programmable spatial light modulator. The former has complex processing technology, and the device can not be erased or programmed. The latter solves the programmability problem, but costs highly. A new idea is proposed in this paper, which is to realize programmable wavefront modulation based on photorefractive effect. Photorefractive effect is a nonlinear optical phenomenon that the refractive index of optical crystals changes with the intensity of writing beam. By establishing the mapping relationship between the light intensity distribution and the refractive index distribution , when a certain refractive index profile is needed, the corresponding writing light will be irradiated on the crystal, realizing the programmable wavefront modulation. Since there is no analytical corresponding relationship between the change of crystal refractive index and the distribution of writing light intensity, we adapt deep neural network to achieve our goal. To reduce the difficulty of network learning, in our experiment, a Gaussian beam is used to irradiate the crystal in a small area , and the mapping between refractive index distribution and Gaussian parameters is established. When performing wavefront modulation, Gaussian beams with different parameters are irradiated on the crystal in a small area region by region, and the refractive index distribution of each writing region can be combined to approximate the target refractive index distribution. In this paper, 12 groups of crystal refractive index distribution images with different Gaussian light parameters are collected. In each group, 100 images are used for training and 20 images are used for testing. The network model adopts the regression model based on resnet18. The experimental results show that the average test relative error of Gaussian light parameters is 0.90%, which proves the feasibility of the method proposed in this paper. Finally, the paper uses the leaving one out method for cross validation to analyze the generalization ability of the network model.