Biography
I am a Ph.D. student at the Department of Biomedical Engineering, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, USA, co-advised by Prof. Ge Wang and Prof. Pingkun Yan at the Biomedical Imaging Center. My current research focuses on medical imaging and multimodal analytical frameworks that jointly leverage CT imaging, genetic data, and clinical variables to improve CVD risk prediction. Previously, I obtained my B.Sc. in Physics from the University of Science and Technology of China. In my undergraduate studies, I focused on wavefront modulation methods using deep learning, under the supervision of Prof. Xiaoye Xu and Prof. Zhiwei Xiong.
Prof. Ge Wang’s Lab: AI-based X-ray Imaging System (AXIS) lab
Prof. Pingkun Yan’s Lab: Deep Imaging Analytics Lab (DIAL)
- Medical physics
- Medical imaging
- Medical image analysis
- Deep learning
- Network interpretability
Ph.D. Student in Biomedical Engineering, 2022-present
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
B.Sc. in Physics, 2022
University of Science and Technology of China
Featured Publications
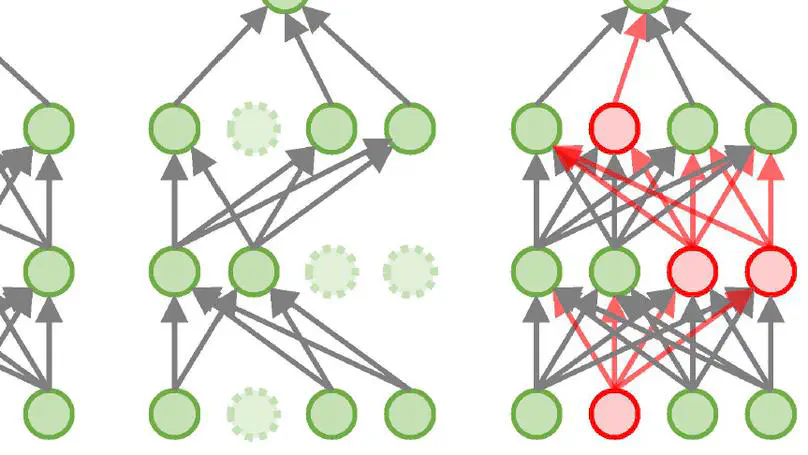
Flipover, an enhanced dropout technique, is introduced to improve the robustness of artificial neural networks. In contrast to dropout, which involves randomly removing certain neurons and their connections, flipover randomly selects neurons and reverts their outputs using a negative multiplier during training. This approach offers stronger regularization than conventional dropout, refining model performance by (1) mitigating overfitting, matching or even exceeding the efficacy of dropout; (2) amplifying robustness to noise; and (3) enhancing resilience against adversarial attacks. Extensive experiments across various neural networks affirm the effectiveness of flipover in deep learning.
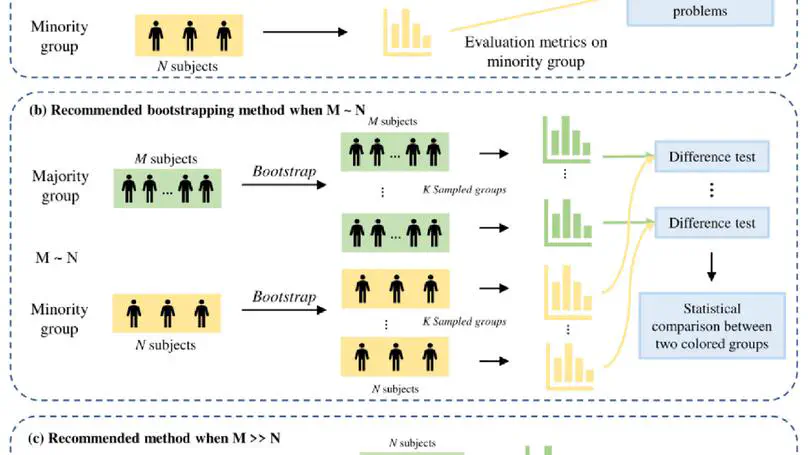
Fairness of artificial intelligence and machine learning models, often caused by imbalanced datasets, has long been a concern. While many efforts aim to minimize model bias, this study suggests that traditional fairness evaluation methods may be biased, highlighting the need for a proper evaluation scheme with multiple evaluation metrics due to varying results under different criteria. Moreover, the limited data size of minority groups introduces significant data uncertainty, which can undermine the judgement of fairness. This paper introduces an innovative evaluation approach that estimates data uncertainty in minority groups through bootstrapping from majority groups for a more objective statistical assessment. Extensive experiments reveal that traditional evaluation methods might have drawn inaccurate conclusions about model fairness. The proposed method delivers an unbiased fairness assessment by adeptly addressing the inherent complications of model evaluation on imbalanced datasets. The results show that such comprehensive evaluation can provide more confidence when adopting those models.
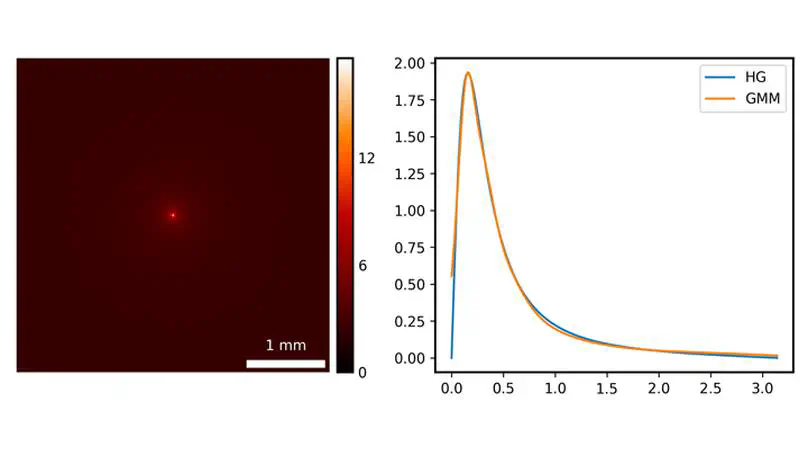
Objective. The phase function is a key element of a light propagation model for Monte Carlo (MC) simulation, which is usually fitted with an analytic function with associated parameters. In recent years, machine learning methods were reported to estimate the parameters of the phase function of a particular form such as the Henyey–Greenstein phase function but, to our knowledge, no studies have been performed to determine the form of the phase function. Approach. Here we design a convolutional neural network (CNN) to estimate the phase function from a diffuse optical image without any explicit assumption on the form of the phase function. Specifically, we use a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) as an example to represent the phase function generally and learn the model parameters accurately. The GMM is selected because it provides the analytic expression of phase function to facilitate deflection angle sampling in MC simulation, and does not significantly increase the number of free parameters. Main Results. Our proposed method is validated on MC-simulated reflectance images of typical biological tissues using the Henyey–Greenstein phase function with different anisotropy factors. The mean squared error of the phase function is 0.01 and the relative error of the anisotropy factor is 3.28%. Significance. We propose the first data-driven CNN-based inverse MC model to estimate the form of scattering phase function. The effects of field of view and spatial resolution are analyzed and the findings provide guidelines for optimizing the experimental protocol in practical applications. Summary. We developed the first data-driven CNN-based inverse Monte Carlo model to estimate the form of scattering phase function. The findings provide guidelines for optimizing the experimental protocol in practical applications.
Publications
Projects
Contact
Please leave a message if you have any questions.
- liangy15@rpi.edu
- 110 8th Street, Troy, NY 12180
- 4231 Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies Building